Research
분자동역학 시뮬레이션 (Molecular Dynamics Simulation)
분자 동역학(MD; Molecular Dynamics) 시뮬레이션은 고전 역학을 기반으로 하며 평형 또는 비평형 상태에 있는 분자들의 반응과 에너지 또는 여러 성질들을 알아볼 수 있는 컴퓨터 시뮬레이션 화학이다. 예를 들어, 용액내 존재하는 이온들의 상호작용과 용매와 이온간의 상호작용을 알아볼 수 있으며 이를 통해 시뮬레이션의 값과 실험값을 비교하여 데이터의 근거를 제시할 수 있으며 실험을 통해 알지 못하는 부분 또한 시뮬레이션으로 방향을 제시할 수 있다.
Molecular Dynamics (MD) simulation is a computer simulation technique in chemistry that is based on classical mechanics and enables the investigation of the behavior, energy, and various properties of molecules in equilibrium or non-equilibrium states. For instance, it allows the study of interactions among ions present in a solution and between solvents and ions. By comparing simulation results with experimental data, MD simulations can provide a basis for the interpretation of experimental findings, as well as suggest directions in cases where experimental information is lacking.
-
Energy Transfer Rate Calculation with Hybrid Monte Carlo Simulation
MD 시뮬레이션을 통해 OLED의 발광층에서의 에너지 및 전하 전달 과정에 대한 정보를 얻을 수 있다. 예를 들어, OLED소자에서의 유기물 증착 과정을 모사한 MD 시뮬레이션을 통해 host medium에 dopant가 첨가된 구조를 생성한 후, dopant 간의 상대적 거리, transition dipole moment의 배향, 흡수/발광 스펙트럼 등의 정보를 기반으로 hybrid Monte Carlo 시뮬레이션을 진행하여 dopant 분자들 간의 Föster energy transfer (FRET) 속도상수 (kFRET)를 결정할 수 있다. 위 결과에서는 dopant 농도가 증가할 수록 kFRET의 값이 점점 커지는 것을 확인했고, 이 결과는 실험값과 그 경향이 일치하는 것을 알 수 있었다.
Through MD simulations, information about energy and charge transfer processes in the emissive layer of OLEDs can be obtained. For instance, by simulating the organic deposition process of the emissive layer of OLED devices using MD simulations, a structure with a dopant added to the host medium can be generated. Based on information such as the relative distance between dopants, orientation of transition dipole moments, and absorption/emission spectra, a hybrid Monte Carlo simulation can be conducted to determine the Förster energy transfer (FRET) rate constant (kFRET) among dopant molecules. The above results showed that as the dopant concentration increases, the value of kFRET progressively increases, which was found to be consistent with experimental observations.
Reference: J. Mater. Chem. C. 2021, 9, 15141-15149 (Link)
-
Investigation of Molecular Packing Mechanisms
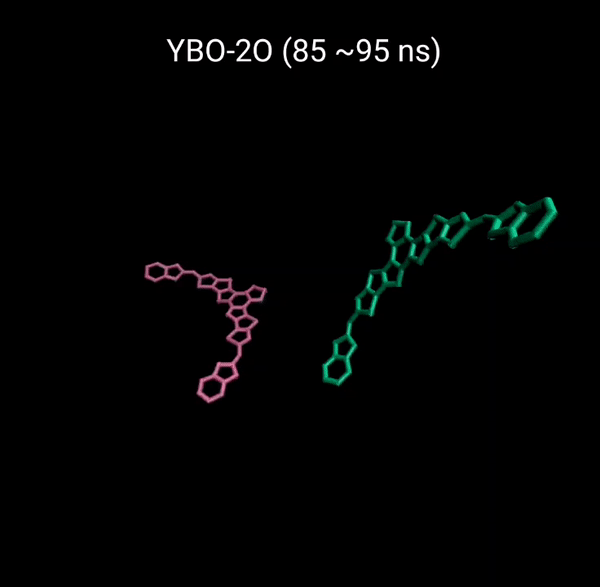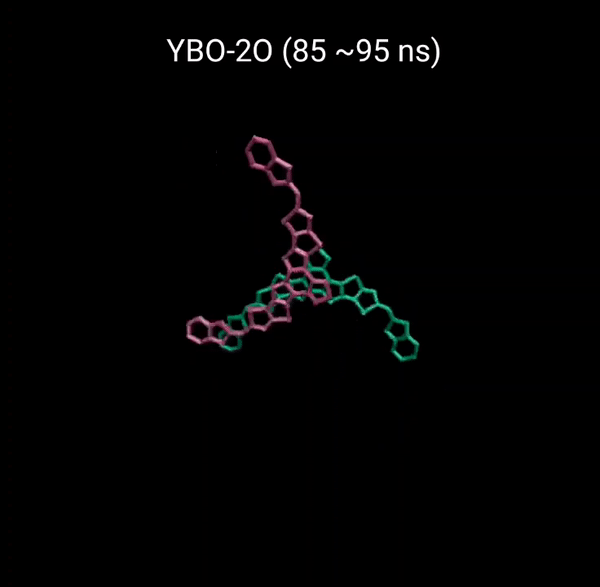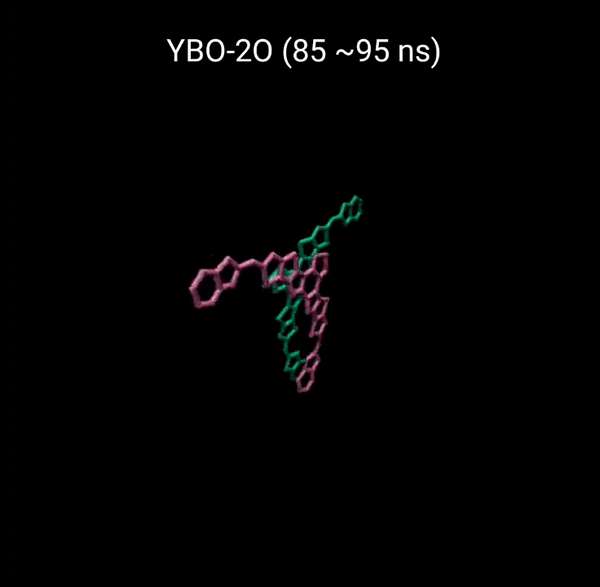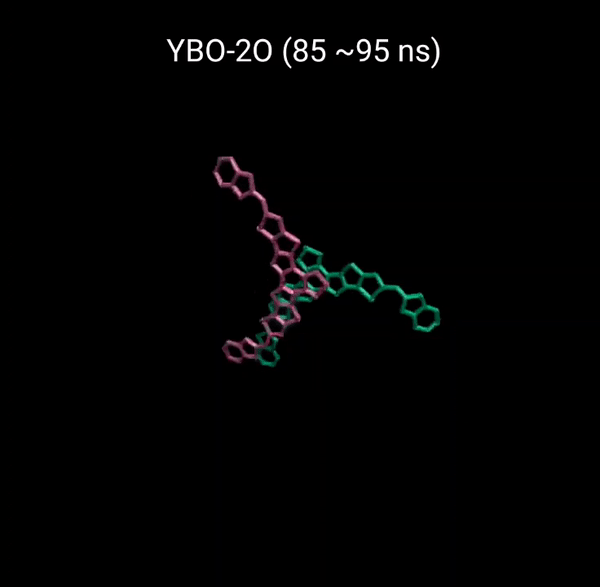
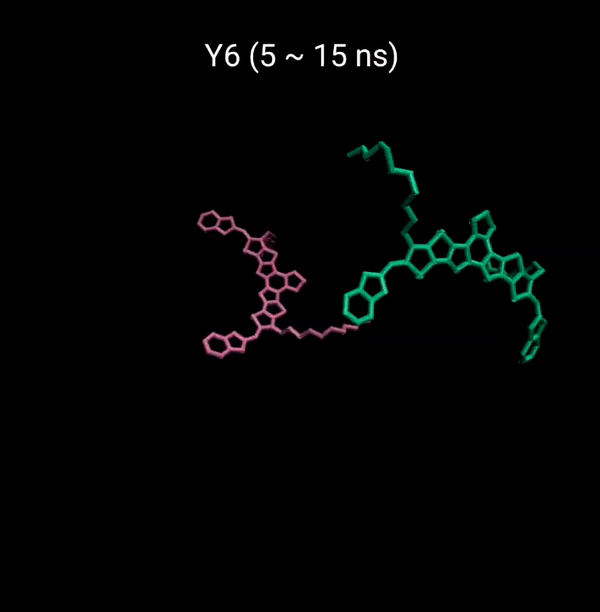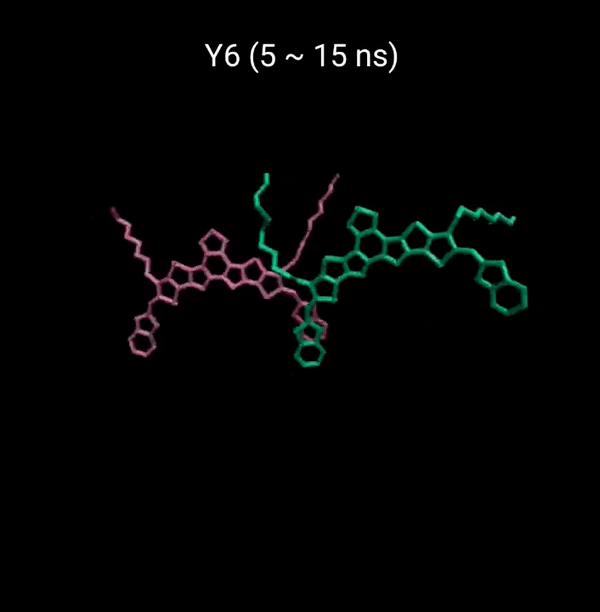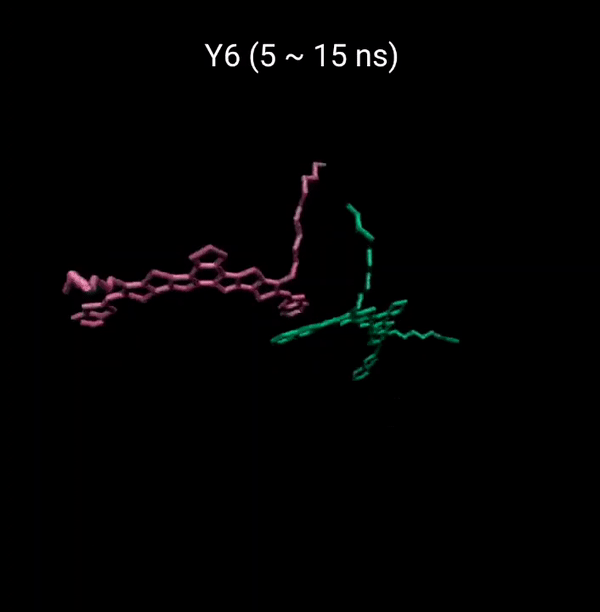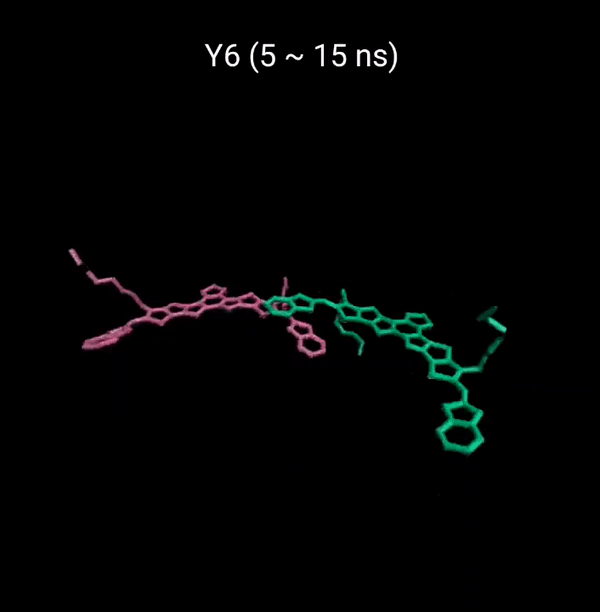
MD 시뮬레이션을 통해 분자의 패킹 형성 매커니즘을 분석할 수 있다. 유기반도체는 분자구조에 알킬체인이 치환됨으로서 유기용매에 대한 용해성을 갖는다. 또한 이러한 알킬체인은 분자의 패킹구조에 알킬체인이 말단기에 치환되어 있는 경우 (YBO), 안정한 패킹 구조 (CC-TT)의 형성이 용이하지만, 알킬체인이 코어에 치환되어 있는 경우 (Y6), 알킬체인의 스테릭 방해로 인해 안정한 CC-TT 구조의 형성이 어려움을 알 수 있다.
Molecular Dynamics (MD) simulation can be employed to analyze the packing formation mechanism of molecules. In the case where alkyl chains are substituted at the terminal groups (YBO), the formation of a stable packing structure (CC-TT) is facilitated. However, when the alkyl chains are substituted at the core (Y6), the formation of a stable CC-TT structure is hindered due to steric hindrance caused by the alkyl chains.
Reference: