Research
기계 학습/심층 학습을 기반으로 매우 많은 종류의 분자와 그 해당 성질을 모아둔 데이터베이스를 활용해 분자 구조와 그 성질을 연관 짓는 규칙을 얻을 수 있고, 임의의 분자의 성질을 학습된 규칙을 통해 예측할 수 있다.
또한, 특정한 분자 구조의 성질을 예측하는 것 뿐만 아니라 심층 학습/강화 학습을 기반으로 원하는 특성을 지닌 분자를 설계할 수 있다.
Machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) techniques enable the extraction of structure–property relationships from large-scale molecular databases, allowing accurate prediction of properties for arbitrary molecules.
Furthermore, DL-based generative models, including reinforcement learning (RL), can be employed to design novel molecules with target properties in a data-driven approach
다양한 시분해 분광 실험을 통해 분자 수준에서의 동력학을 연구할 수 있다. 빛을 흡수하여 들뜬상태가 된 분자계는 다양한 이완 과정을 거쳐서 바닥상태로 이완 되거나, 추가적인 광물리적 과정을 거쳐서 화학반응을 유발하게 된다. 광유발 물리적/화학적 과정은 짧게는 펨토초 또는 피코초 시간영역에서 길게는 밀리초 시간영역에서 일어나며, 시분해 분광법을 활용해서 효과적으로 연구될 수 있다.
Various time-resolved spectroscopic experiments can be employed to investigate the dynamics at the molecular level. Upon absorption of light, excited molecular states undergo various relaxation processes, returning to the ground state or initiating chemical reactions through additional photophysical/chemical pathways. These photoinduced physical/chemical processes occur in time domains ranging from femtoseconds or picoseconds to milliseconds, and can be effectively studied using time-resolved spectroscopy techniques.
양자 화학 계산 기법을 이용하여 다양한 분자의 분자 구조, 분자의 에너지 레벨, HOMO와 LUMO, 분자의 진동 모드, IRC 등을 계산할 수 있다. 또한 계산 결과를 통해 실제로 일어나는 분자의 동력학을 예측할 수 있다.
Using quantum chemical calculation techniques, various molecular properties such as molecular structure, energy levels, HOMO and LUMO orbitals, molecular vibrational modes, and IRC can be computed. Additionally, computational results can be used to predict the dynamics of molecules.
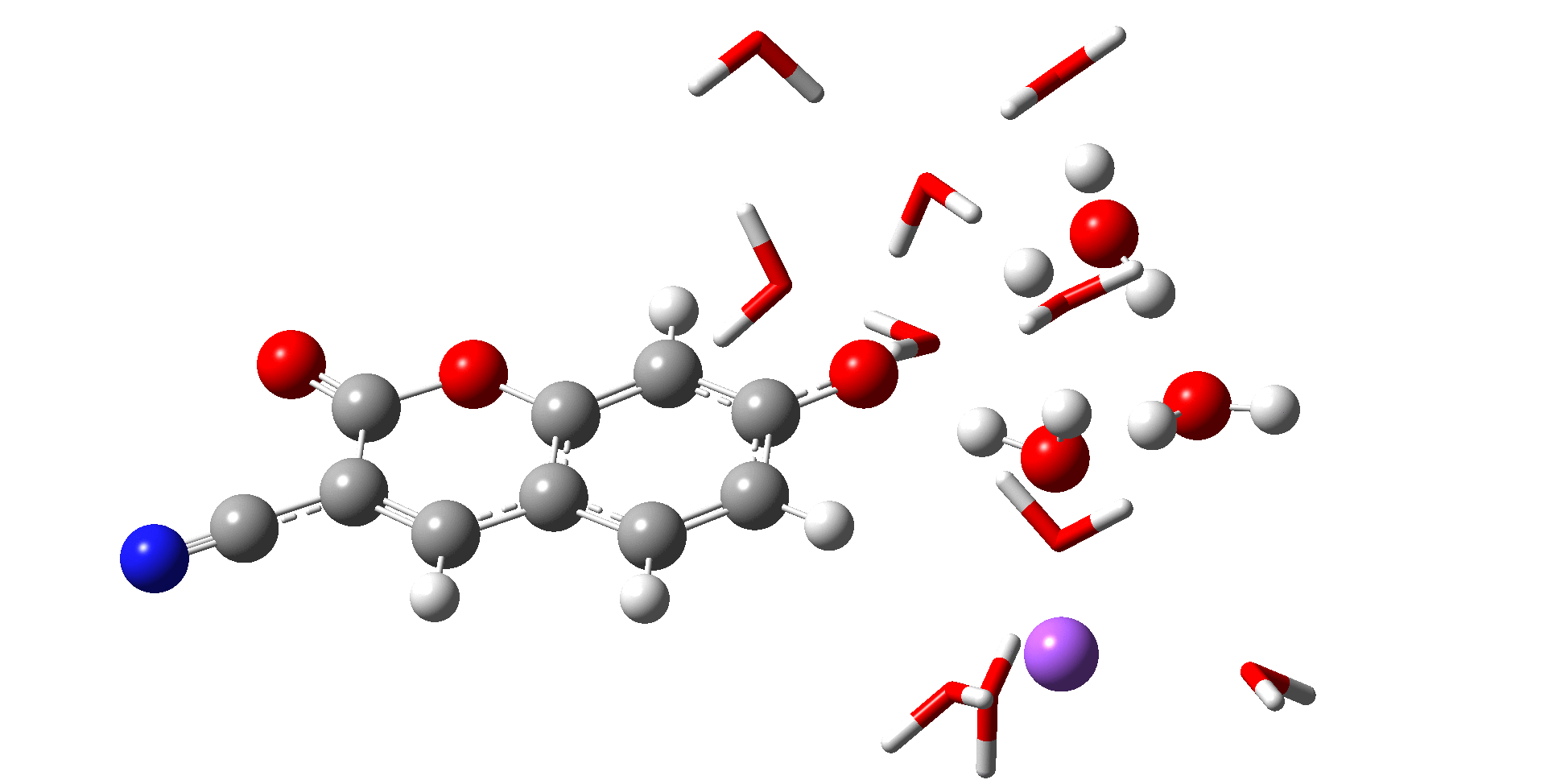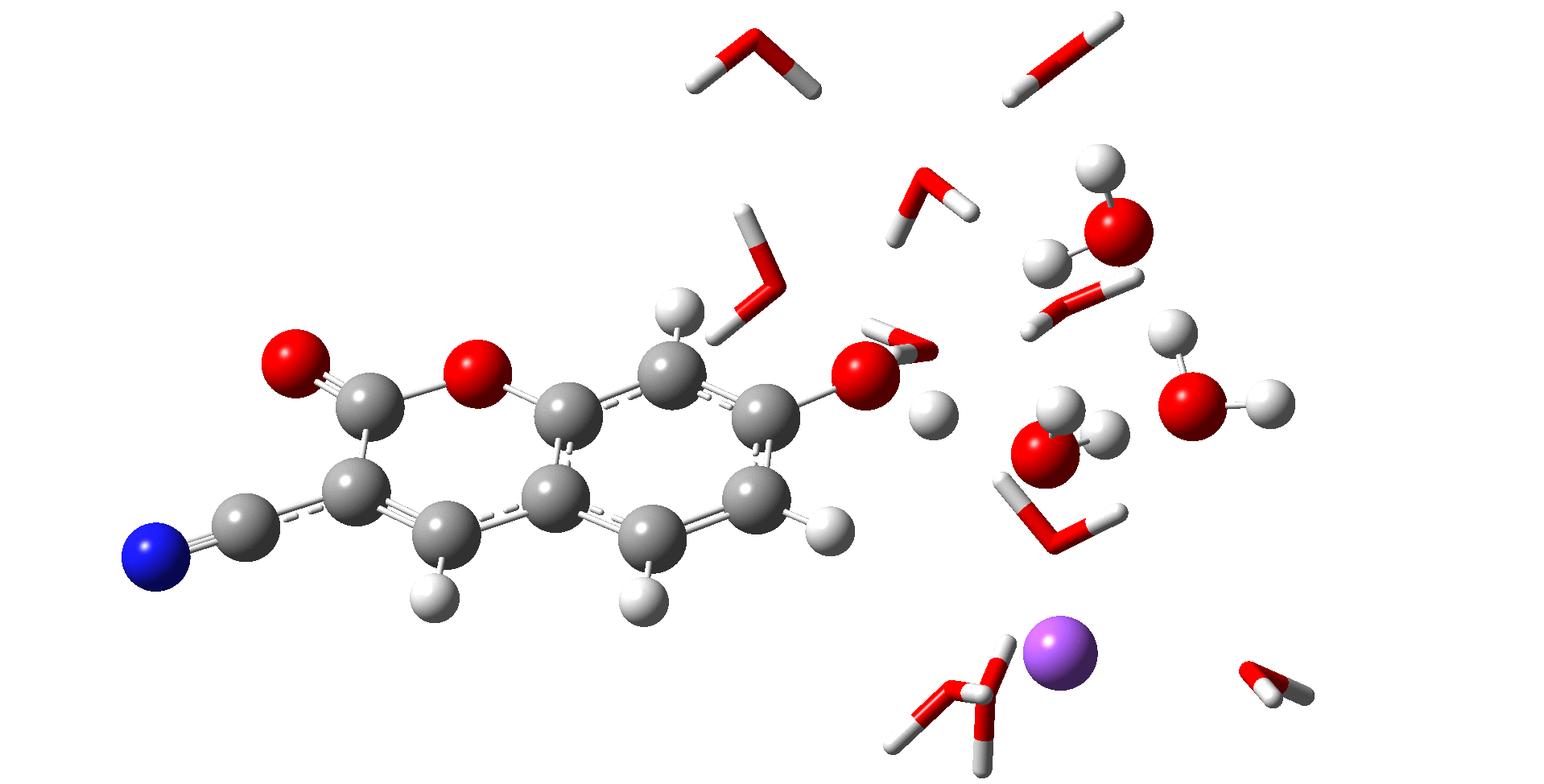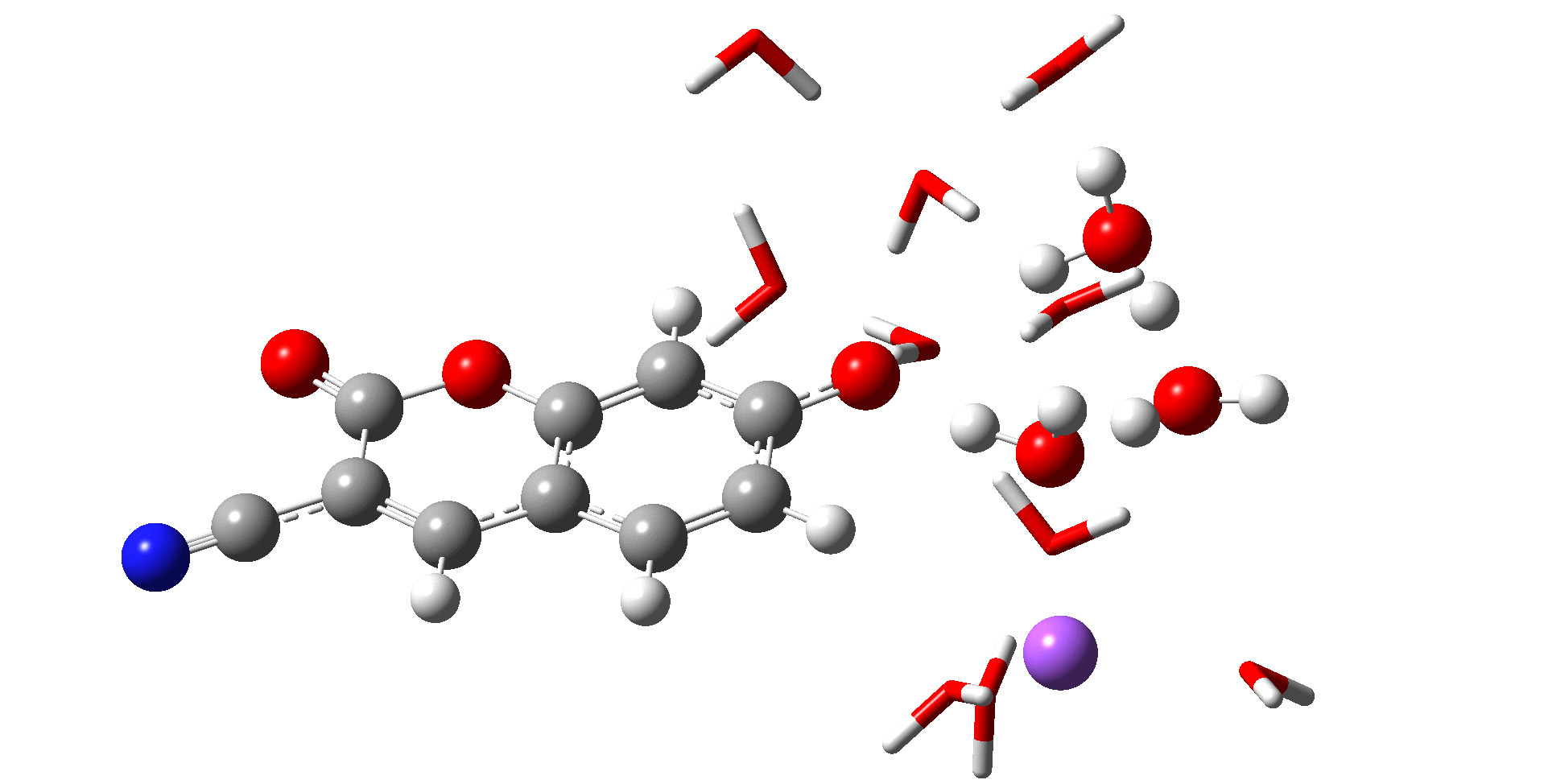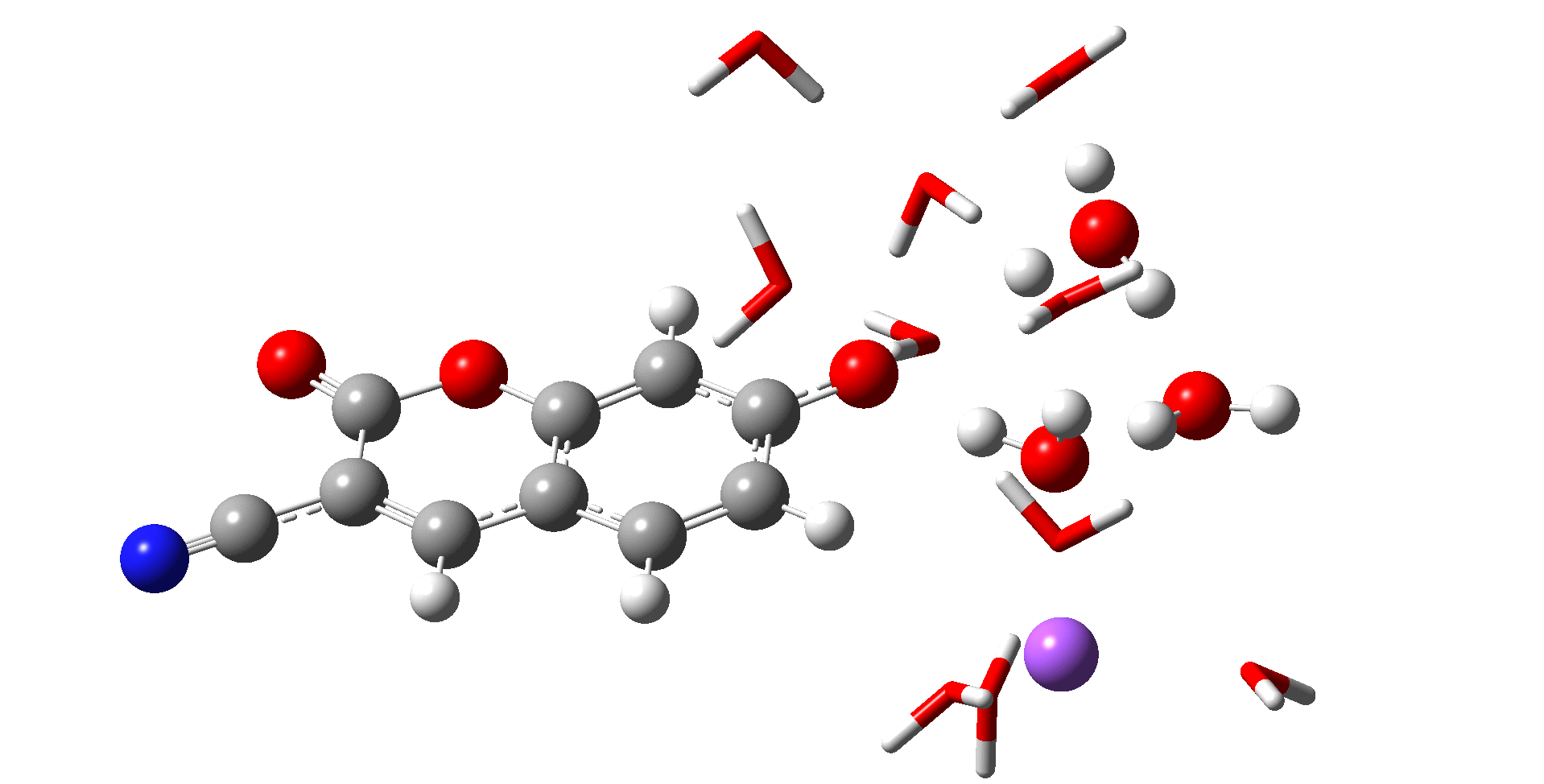
분자 동역학(MD; Molecular Dynamics) 시뮬레이션은 고전 역학을 기반으로 하며 평형 또는 비평형 상태에 있는 분자들의 반응과 에너지 또는 여러 성질들을 알아볼 수 있는 컴퓨터 시뮬레이션 화학이다. 예를 들어, 용액내 존재하는 이온들의 상호작용과 용매와 이온간의 상호작용을 알아볼 수 있으며 이를 통해 시뮬레이션의 값과 실험값을 비교하여 데이터의 근거를 제시할 수 있으며 실험을 통해 알지 못하는 부분 또한 시뮬레이션으로 방향을 제시할 수 있다.
Molecular Dynamics (MD) simulation is a computer simulation technique in chemistry that is based on classical mechanics and enables the investigation of the behavior, energy, and various properties of molecules in equilibrium or non-equilibrium states. For instance, it allows the study of interactions among ions present in a solution and between solvents and ions. By comparing simulation results with experimental data, MD simulations can provide a basis for the interpretation of experimental findings, as well as suggest directions in cases where experimental information is lacking.